- Location
- Trexler 363
- Times
- MWF 3:30 - 5:30 pm
- Office Hours
- M-Th 2 - 3pm
- Office
- Trexler 365B
- chssmith AT roanoke DOT edu
Test 1
$ mkdir ~/cs170/tests $ mkdir ~/cs170/tests/test1 $ cd ~/cs170/test/test1
This portion of the test is worth 30 total points. In addition to this file, you may only access the Python documentation website and the graphics documentation documentation website. NO OTHER WEBSITES ARE PERMITTED. You are also not allowed to access any personal files in your CS account. As usual, you are not allowed to directly copy any code from the Internet or another individual. You should also follow all coding standards discussed thus far.
C++ Activities
Question 9
Create a class called Simulator. This class should
have attributes PC, R1, and
R2. All three attributes should be integers, and
should be defaulted to the value 0.
This class should have methods called add and
sub, which performs the specified operations on R1 and
R2 (in that order, so R1 - R2), and stores the result in attribute
R1. Each operation should increment the PC attribute by 1.
You should also provide methods called set_R1 and
set_R2, which allow the values of R1 and R2 to be set,
respectively. Include a print() method which
simply prints the values of all of the registers in table format.
Simulator my_sim; my_sim.set_R1(3); my_sim.set_R2(4); my_sim.add(); my_sim.print(); //Prints: // R1 7 // R2 4 my_sim.sub(); my_sim.print(); //Prints: // R1 3 // R2 4
(10 points)
Question 10
Create a class called
AdvancedSimulator, which inherits
your above definition of Simulator. This should add
two additional attributes: R3 and R4.
These should also be integers, but their values should be provdied to
the constructor. You
should define appropriate methods for setting these registers as
well. You need to define methods to copy the value from R3 or R4
into R2. These methods should be named following the template
copy_R#_to_R2. You also need to add two additional
methods: mul
and div, which computes the product and quotient
(integer!) of R1 and R2 (respectively), and stores them in the R1
attribute.
Every one of these operations should increment the PC attribute.
Don't forget to override the print() method so
that it can print all 4 registers!
AdvancedSimulator my_adv_sim(1, 2); my_adv_sim.set_R3(2); my_adv_sim.set_R1(3); my_adv_sim.set_R2(4); my_adv_sim.add(); my_adv_sim.print(); //Prints: // R1 7 // R2 4 // R3 2 // R4 2 my_adv_sim.sub(); my_adv_sim.print(); //Prints: // R1 3 // R2 4 // R3 2 // R4 2 my_adv_sim.copy_R4_to_R2(); my_adv_sim.print(); //Prints: // R1 3 // R2 2 // R3 2 // R4 2 my_adv_sim.mul(); my_adv_sim.print(); //Prints: // R1 6 // R2 2 // R3 2 // R4 2 my_adv_sim.div(); my_adv_sim.print(); //Prints: // R1 3 // R2 2 // R3 2 // R4 2
(10 points)
Python Activity
Question 11
Create a file called Gradebook.py which will implement a
class called Gradebook. This class should have an
attribute which is a dictionary, which will associate the name of a
student with a list of grades that student earned. Your class
should have a method add_student, which takes a
students name as a parameter and adds a new, empty list to the
gradebook dictionary. It should also have a
method add_grade, which takes a students name, and an
integer representing their grade. It should add the grade to the
list with the associated student.
You should also have a method get_grades, which takes a
students name and returns the list of grades associated with that student.
gradebook = Gradebook.Gradebook()
gradebook.add_student("Scotty")
gradebook.add_student("Bouchard")
gradebook.add_grade("Scotty", 20)
gradebook.add_grade("Bouchard", 100)
gradebook.add_grade("Scotty", 50)
gradebook.add_grade("Bouchard", 99)
print(gradebook.get_grades("Scotty")) #Prints: [20, 50]
print(gradebook.get_grades("Bouchard")) #Prints: [100, 99]
(10 points)
Challenge
In a file called Star.py,
Create a class that can be used to represent a 6-pointed
Star. You need at least attributes for the x
and y coordinates of the star, which should be
roughly centered on the star. It should also have a
method draw, which draws the star using the
graphics module.
Create a python program that uses the graphics module and demonstrates that your class is written correctly.
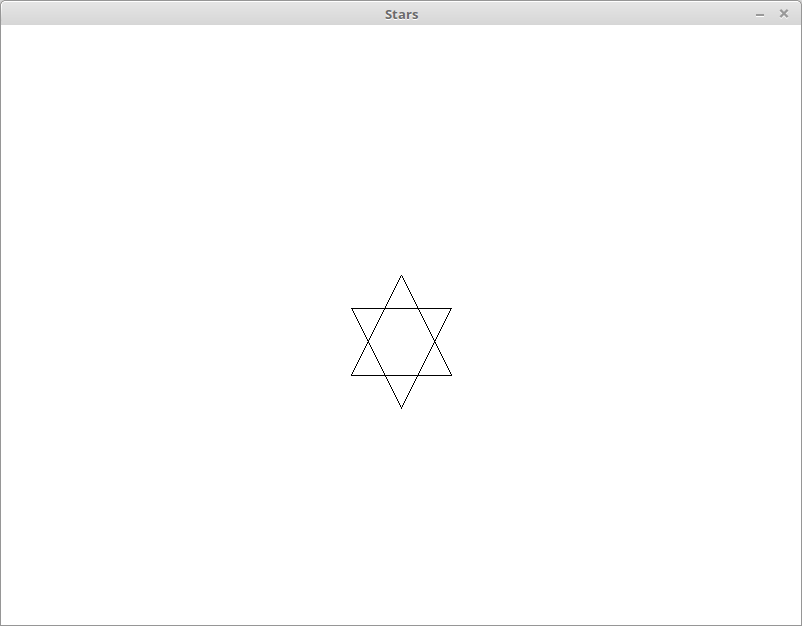
(5 points)
Submission
When you have finished, create a tar file of your test1
directory. To create a tar file, execute the following commands:
cd ~/cs170/tests tar czvf test1.tgz test1/
To submit your activity, go to inquire.roanoke.edu. You should
see an available assignment called Test 1.
Make sure you include a header listing the authors of the file.