5.3. The math module¶
The math module contains the kinds of mathematical functions you would typically find on your
calculator and some mathematical constants
like pi and e.
As we noted above, when we import math, we create a reference to a module object that contains these elements.
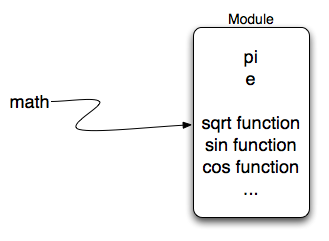
Here are some items from the math module in action. If you want more information, you can check out the Math Module Python Documentation.
Notice another difference between this module and our use of turtle.
In turtle we create objects (either Turtle or Screen) and call methods on those objects. Remember that
a turtle is a data object (recall alex and tess). We need to create one in order to use it. When we say
alex = turtle.Turtle(), we are calling the constructor for the Turtle class which returns a single turtle object.
Mathematical functions do not need to be constructed. They simply
perform a task.
They are all housed together in a module called math. Once we have imported the math module, anything defined there
can be used in our program. Notice that we always use the name of the module followed by a dot followed by the
specific item from the module (math.sqrt). You can think of this as lastname.firstname where the lastname is the module
family and the firstname is the individual entry in the module.
If you have not done so already, take a look at the documentation for the math module.
Check your understanding
-
modules-3-1: Which statement allows you to use the math module in your program?
- (A) import math
- The module must be imported before you can use anything declared inside the module.
- (B) include math
- The correct term is not include, but you are close.
- (C) use math
- You will be using parts of the module, but that is not the right term.
- (D) You don't need a statement. You can always use the math module
- You cannot use a Python module without a statement at the top of your program that explicitly tells Python you want to use the module.