- Location
- Trexler 363
- Times
- MWF 12:00 - 2:10 pm
- Office Hours
- M-Th 5 - 6pm
- Office
- Trexler 365B
- chssmith AT roanoke DOT edu
Lab 8: Nested Loops
As usual, create a directory to hold today's files. All programs that you write today should be stored in this directory.
$ cd ~/cs120/labs $ mkdir lab8 $ cd lab8
Write a Python program that uses nested for loops to print the numbers 1 through 9 in three rows. The numbers should be separated by spaces.
Example
$ python3 practice1.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Write a Python program that uses nested for loops to print 10 rows of asterisks where each row has one fewer asterisk than the row preceeding it.
Example
$ python3 practice2.py ********** ********* ******** ******* ****** ***** **** *** ** *
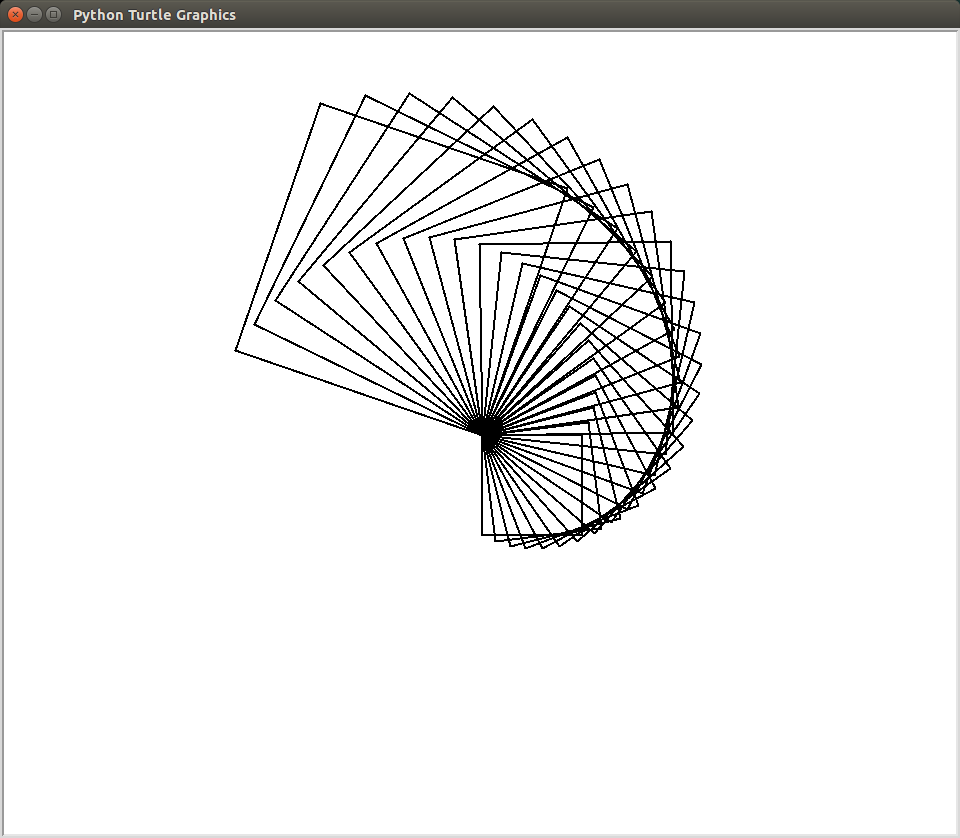
A Nautilus is a sea creature whose shell is very well studied in the field of mathematics. As it turns out, a nautilus shell exhibits properties not only of the golden ratio, but also of fractal like patterns. Today, you will use a nested for loop to replicate the visual appearance of a nautilus shell.
Details
In Emacs, create a Python program in a file called nautilus.py that uses turtle graphics to draw a series of rotated squares to approximate a nautilus shell.
Example
$ python3 nautilus.py
Hint
This program requires the use of a nested for loop.
-
The outer loop determines how many squares are drawn.
-
The inner loop should draw a single square. The outer loop iterator variable should be used to determine the size of the square.
-
After drawing the square, but still but still inside the outer loop, the turtle should turn so that the next square will be drawn slightly rotated.
Challenge
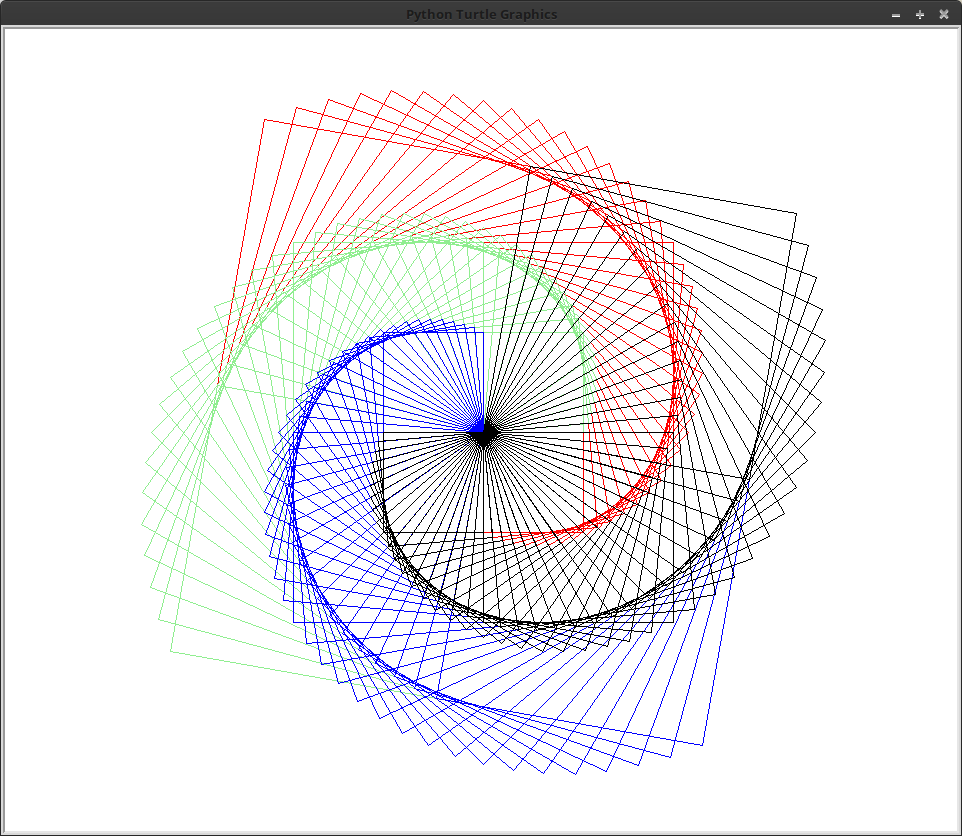
Simply repeating this shape several times can create even more
interesting patterns than the one you see above. Add another loop
to your program which will cause the above pattern to execute 4
times. Each nautilus should start at a 90° offset from where
the previous nautilus started. Use this outer loop to modify the color of the turtle for
an even more impressive design. You may need to
use setheading
for this activity.
Nesting for loops can be confusing. Sometimes, it is better to have a simple example to get a better understanding of how things work. However, we can't let you fully off the hook, mathematically. Printing a pyramid that looks pretty can be slightly challenging, but if you keep track of the number of spaces and letter necessary you should figure out mathematically what is going on.
Details
In Emacs, create a Python program in a file called pyramid.py that prints to the terminal a pyramid of asterisks. It should prompt the user for the number of levels to print.
Test your program by running it multiple times with different input values. Make sure your code follows the courses code conventions.
Example
$ python3 pyramid.py
Enter the number of levels: 6
*
* *
* * *
* * * *
* * * * *
* * * * * *
Hint
-
This program is going to need a total of 3 loops, two loops nested inside another loop. The outer for loop will execute for the number of levels in the pyramid. The first for loop inside the outer loop prints the spaces that preceed the askerisks on that level. The second loop inside the outer loop prints asterisks.
-
The number of askerisks is directly related to the level of the pyramid. If the top of the pyramid is level 1, then the number of asterisks is the same level number.
-
The number of spaces is inversely related to the level of the pyramid. If the top of the pyramid is level 1, then the number of spaces is the number of levels minus the level number.
-
In order to get multiple things printed on a single line in python, we have to take advantage of a special option of the print function called end. end lets us specify what appears at the end of the statement we want printed, and defaults to the newline character.
If I don't want a newline at the end of my print statement, I just change the value of end in my call to the print function:
print("anything", "to", "print", end="")When you want to add a new line later in your program, you can simply call print again.