- Location
- Trexler 363
- Times
- MWF 12:00 - 2:10 pm
- Office Hours
- M-Th 5 - 6pm
- Office
- Trexler 365B
- chssmith AT roanoke DOT edu
Lab 13: Functions
As usual, create a directory to hold today's files. All programs that you write today should be stored in this directory.
$ cd ~/cs120/labs
$ mkdir lab13
$ cd lab13
Practice 1
Write a function
called equilateral_area(edge_length)
that computes the area of an equilateral triangle with the
specified
edge length.
Practice 2
Copy and paste your solution to the previous exercise into
this one,
and use it when writing a function
called sierpinski_area(edge_length) that computes
the
area of a Sierpinski triangle of order one. A Sierpinski
Triangle of
order one is an equilateral triangle with a triangular hole.
The
vertices of the hole triangle are the mid points of the
Sierpinski
triangle's edges. For example:
Note: The editor boxes on this page use the Emacs shortcuts for copy and paste. Copy is Alt-W (M-W), and paste is Ctrl-y (C-y).
When working with functions, abstraction is key. You will soon find yourself in a position where you start thinking about problems in functions. Being able to break a complex problem, like an advanced drawing, into smaller and simpler problems which can be solved with a function can make your code a lot easier to write, and a lot easier to read.
Details
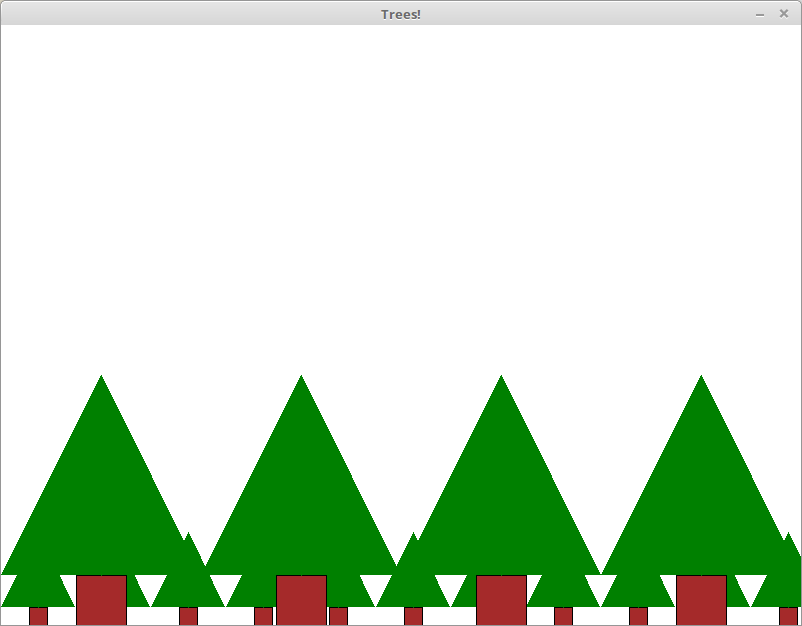
Create a function draw_tree(x_location, y_location) in
a file called forest.py. The function should use
the graphics
module to draw a tree. The x and y location specified is the center
of the base of the triangle making up the tree. The tree should
look like the tree in the example below.
Notice that a tree is defined by a brown square, and a filled green
triangle. For this, define one additional
function in the same file. This second function should be
called
draw_triangle(x_location, y_location),
which creates a filled, green isosceles triangle of some globally
defined height. For this triangle, the height of the triangle is the
same as the length of the base of the triangle.
Note that there is no mechanism for drawing a filled triangle using the graphics module. You can simulate drawing a filled triangle by drawing several lines from the apex of the triangle to the base of the triangle. If you specify the line thickness accordingly, you will end up with a filled triangle.
Test your function by calling the function multiple times with different parameters. Make sure your code follows the course's code conventions.
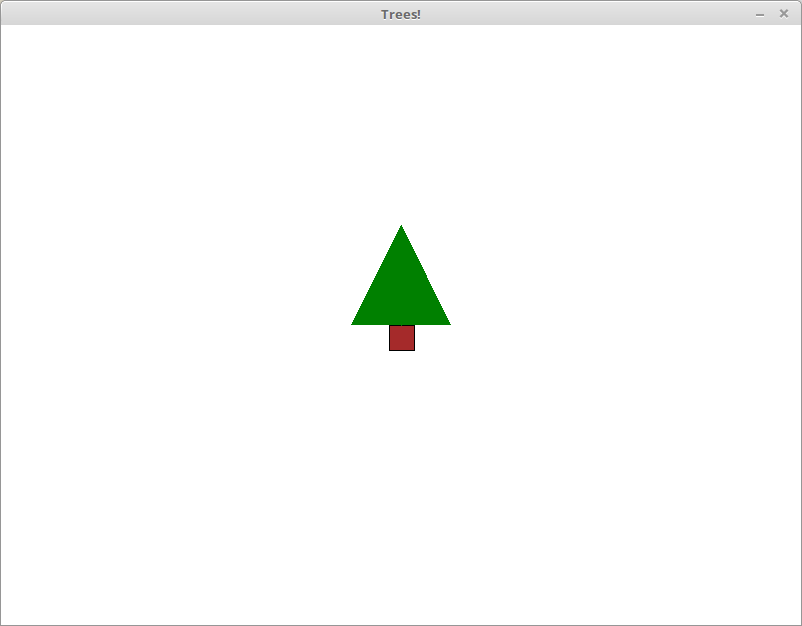
Example Output
graphics.window_size(640, 480) draw_tree(320, 240)
Hint
-
Your
draw_treefunction should consist basically of one call todraw_rectanglefrom the graphics module, and one call todraw_triangle(which you are also writing in this file). - An isosceles triangle is a triangle where two of the sides have the same length. For our particular version of an isosceles triangle, we will say that the two vertical sides have the same length. The height of the triangle will be exactly the same as the width of the triangle.
-
To fill in the triangle, you will compute a series of x coordinates
along the base of the triangle. You can use a for loop to
generate these x coordinates. Inside of this loop, you will
call
draw_lineto connect the top of the triangle to the corresponding point at the bottom of the triangle. The following image is what the tree would look like if we skipped drawing some lines: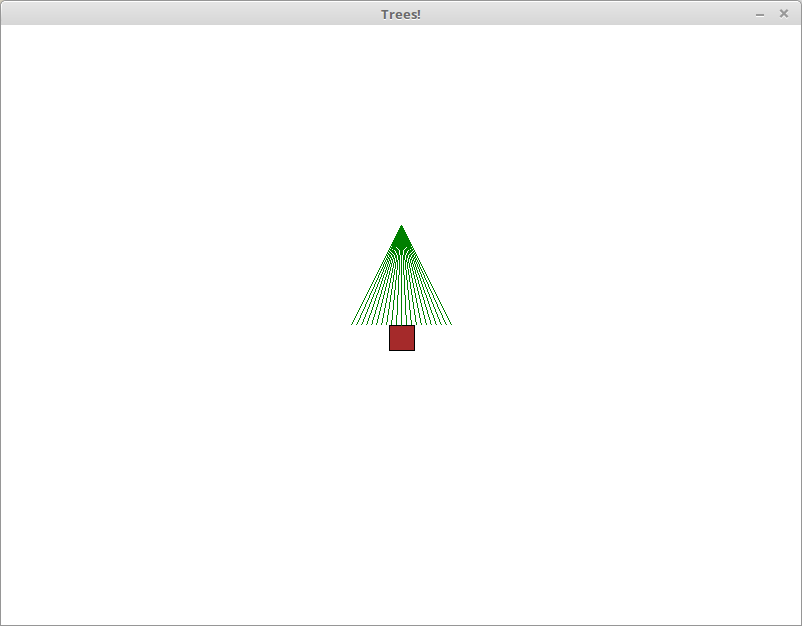
Challenge
Modify your program so that you can specify the size of the tree. We will define the size of the tree to be the witdh of the tree (and the height of the triangle). Use this new function to draw yourself a forest of trees.