Assignment 2: MD5
MD-5 is a cryptographic hash function that is commonly used to compute message digests. These digests are typically used in order ensure data integrity, by comparing the received message to the digest. As long as the hash function is secure, and the digests match, we can have some assurance that the message was unaltered in transit.
The MD5 algorithm is quite straight-forward to implement, just based on the standard specifications. In this assignment, you are going to implement the full protocol, using C++.
Details
MD5 consists of 64 rounds. These 64 rounds are grouped into four 16 round groups, where each group used a unique function F. There are a handful of items that must be hard-coded in your programs. The first set are the initial values of the output vector:
A = 0x67452301 B = 0xefcdab89 C = 0x98badcfe D = 0x10325476
These values make up the 4 initial inputs to the entire algorithm, described in detail below.
Next, the per-round shift amounts, where r is the round number, zero based:
| Round Group | Round F | Message Index | Shift Group | Shift Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 ≤ r ≤ 15 | (B & C) | (!B & D) | g = r | r % 4 == 0 | 7 |
| r % 4 == 1 | 12 | |||
| r % 4 == 2 | 17 | |||
| r % 4 == 3 | 22 | |||
| 16 ≤ r ≤ 31 | (B & D) | (C & !D) | g = (5 × r + 1) % 16 | r % 4 == 0 | 5 |
| r % 4 == 1 | 9 | |||
| r % 4 == 2 | 14 | |||
| r % 4 == 3 | 20 | |||
| 32 ≤ r ≤ 47 | B ⊕ C ⊕ D | g = (3 × r + 5) % 16 | r % 4 == 0 | 4 |
| r % 4 == 1 | 11 | |||
| r % 4 == 2 | 16 | |||
| r % 4 == 3 | 23 | |||
| 48 ≤ r ≤ 63 | C ⊕ (B | !D) | g = (7 × r) % 16 | r % 4 == 0 | 6 |
| r % 4 == 1 | 10 | |||
| r % 4 == 2 | 15 | |||
| r % 4 == 3 | 21 |
And finally, you need an array K of size
64. This array contains a unique value added into each round of the
algorithm. These values can be computed using the sin
function as follows:
K[i] = floor(abs(sin(i + 1)) * pow(2, 32));
The MD5 algorithm begins by padding out the length of the message until its length (in bits) is divisble by 512. This is done by appending a 1, followed by 0's until the length + 64 is divisble by 512. The last 64 bits are filled with the length of the original message, modulo 264.
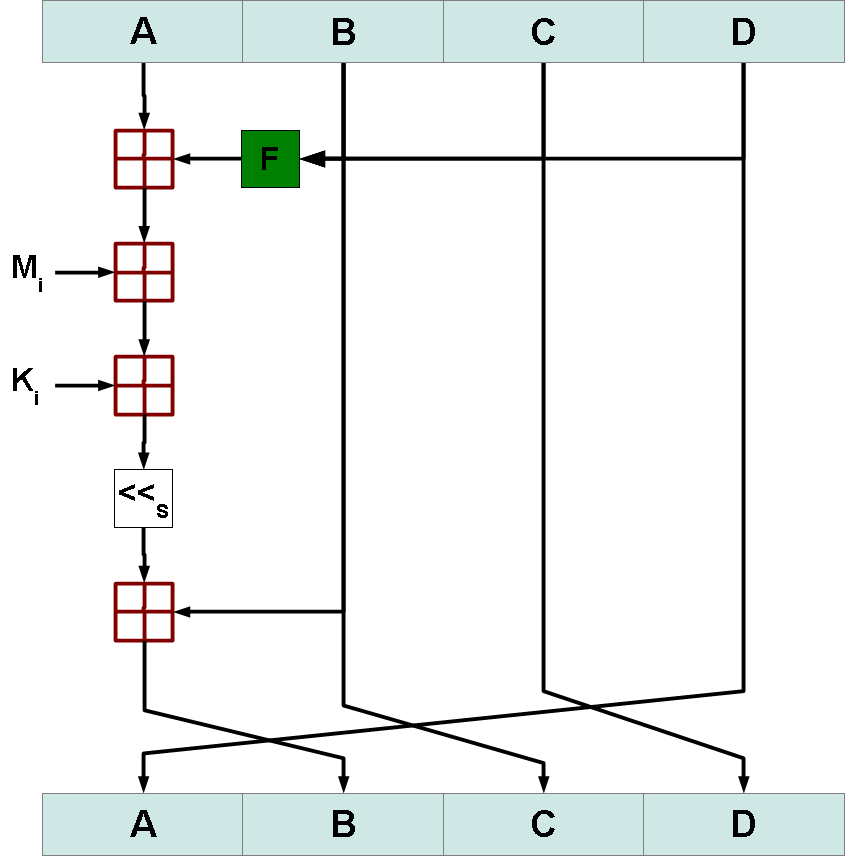 Figure 1: MD5 Single Round
Figure 1: MD5 Single Round
Figure 1 shows a single round of MD5. F, Ki, and s are defined as above. The index i for M is g from the table above. The red boxes represent addition modulo 232.
This round function is executed 64 times per 512 bits of the message. It is sequentially executed on every block of 512 bits. The result of each 512 execution is summed with the previous value of A, B, C, and D.
Specifics
Write a C++ program that compute the MD5 sum of a block of text. Your program should read this block of text from standard input, and write the MD5 sum to standard output in hexadecimal. You can handle the internals of the program however you feel, but the input and output must operate as specified. You can redirect input for your program as follows:
$ ./md5 < input_file cbfdf2ef1934a763484e3d506ca47ae4 $
This assignment is due Thursday, October 10th by the beginning of class. You must write this program in C++. Other languages will not be graded. You should follow all typical code conventions, which can be found at CPSC 120 course website. Specifically you should avoid memory leaks and magic numbers, and include Pre and Post conditions for all defined functions. Submissions will be made through cseval.roanoke.edu.
Last modified: Thu Sep 12 09:23:06 EDT 2013